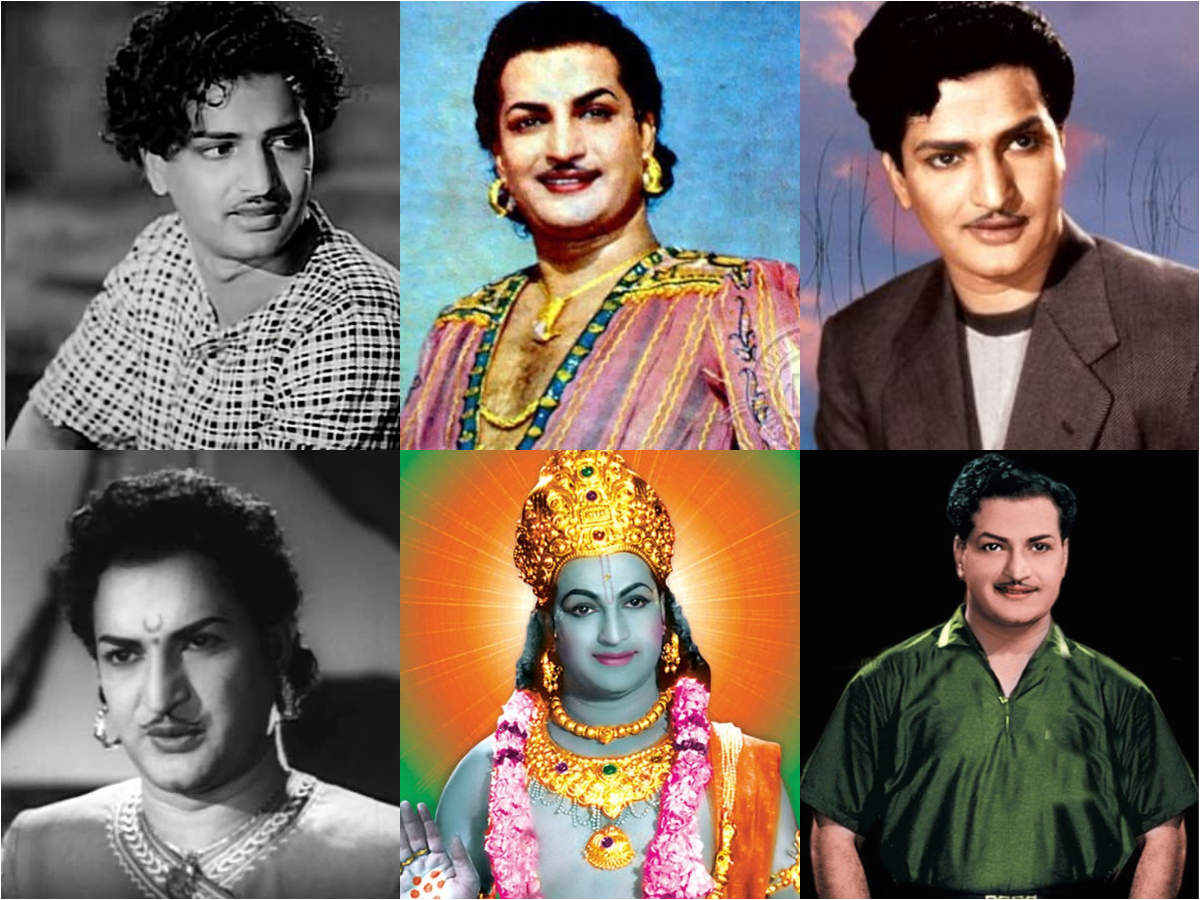
1923 - Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao was a prominent Indian actor, filmmaker, and politician. He was born on May 28, 1923, in Nimmakuru, Andhra Pradesh, India.
Nandamuri Taraka Rama Rao (NTR) was born on May 28, 1923, in Nimmakuru, Andhra Pradesh, India. He was a prominent Indian actor, filmmaker, and politician. He starred in over 300 films, predominantly in Telugu cinema,
and was referred by the media as Viswa Vikhyatha Nata Sarvabhouma (transl. Universally-renowned star of acting). Rao received three National Film Awards for co-producing Thodu Dongalu (1954) and Seetharama Kalyanam (1960) under National Art Theater, Madras, and for directing Varakatnam (1970).In 1982, Rao founded the Telugu Desam Party (TDP) and became the Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh in 1983. He served as Chief Minister for three terms, from 1983 to 1984, from 1984 to 1989, and from 1994 to 1995.
Rao died on January 18, 1996, in Hyderabad, India. He was 72 years old.
NTR is considered one of the most influential figures in Telugu cinema and politics. He is credited with ushering in a new era of Telugu cinema, and his political career inspired many other regional leaders. NTR's legacy continues to inspire people all over the world.
2. 1883 – Vinayak Damodar Savarkar, was an Indian independence activist, poet, writer, and politician. He was born on May 28, 1883, in Bhagur, Maharashtra, India.
Savarkar was born into a Marathi Chitpavan Brahmin family. His father, Damodarpant Savarkar, was a school teacher and his mother, Radhabai Savarkar, was a homemaker. Savarkar had three siblings: Ganesh, Narayan, and Maina.
Savarkar began his activism as a high school student. He was involved in the Indian independence movement and was arrested several times by the British colonial government. In 1906, Savarkar went to London to study law. While in London, he became involved in the Indian independence movement and founded the Free India Society.
In 1910, Savarkar was arrested by the British colonial government and extradited to India. He was sentenced to transportation for life and was sent to the Cellular Jail in Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Savarkar was released from prison in 1924.
After his release from prison, Savarkar continued his activism in the Indian independence movement. He was a leading figure in the Hindu Mahasabha and developed the Hindu nationalist political ideology of Hindutva. Savarkar died on February 26, 1966, in Mumbai, India.
Savarkar is a controversial figure in Indian history. He is revered by some as a hero of the Indian independence movement and a champion of Hindutva. However, he is also criticized by others for his views on violence and his association with the Hindu Mahasabha.
3. 1937: Volkswagen (VW) is founded in Germany.
Volkswagen is a German automotive manufacturer known for producing a wide range of vehicles. Established in 1937, it has become one of the largest automakers globally. Volkswagen offers popular models like the Polo, Golf, Passat, Tiguan, and Touareg. They are actively investing in electric mobility, with the ID series of electric vehicles. Volkswagen aims to become a leader in sustainable transportation and has set targets to reduce carbon emissions. The company focuses on safety, innovation, and digitalization while expanding its global presence. With a rich history and commitment to the future, Volkswagen continues to be a prominent player in the automotive industry.
Today, Volkswagen is one of the largest car manufacturers in the world. The company produces a wide range of vehicles, including cars, trucks, buses, and SUVs. Volkswagen is also a major player in the electric vehicle market.
4. 1961: Amnesty International is founded in London.
Founding of Amnesty International in 1961:
- In 1961, British lawyer Peter Benenson was outraged when he read about two Portuguese students who had been jailed for raising a toast to freedom.
- Benenson wrote an article in The Observer newspaper calling for an amnesty for all prisoners of conscience around the world.
- The article was reprinted in newspapers all over the world and sparked an international movement.
- Amnesty International was officially founded in London in July 1961.
- The organization's mission is to "campaign for the release of all prisoners of conscience, to work for fair and prompt trials for political prisoners, and to end the use of torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment."
- Amnesty International has grown into one of the world's largest and most respected human rights organizations.
- The organization has won numerous awards, including the Nobel Peace Prize in 1977.
Amnesty International continues to work tirelessly to defend human rights around the world. The organization's work is essential to ensuring that everyone, regardless of their beliefs or political views, is treated with dignity and respect.
5. 2008: Nepal votes to abolish their 240-year-old monarchy.
A Brief summary of the 2008 referendum in Nepal that abolished the country's 240-year-old monarchy:
- In 2006, a popular uprising forced King Gyanendra to give up his absolute power.
- A new interim government was formed, and a Constituent Assembly was elected in 2008.
- The Constituent Assembly was tasked with drafting a new constitution for Nepal.
- One of the key issues facing the Constituent Assembly was the future of the monarchy.
- Some people wanted to keep the monarchy, while others wanted to abolish it.
- In May 2008, the Constituent Assembly voted to abolish the monarchy.
- The vote was overwhelmingly in favor of abolition, with 56% of voters supporting the measure.
- The abolition of the monarchy was a major step forward for Nepal.
- It marked the end of centuries of royal rule, and it paved the way for a new era of democracy in Nepal.
The abolition of the monarchy was a historic event, and it was a major victory for the people of Nepal. The monarchy had been a symbol of oppression and inequality, and its abolition was a step towards a more just and democratic society. The people of Nepal had long been yearning for freedom from the monarchy, and the referendum was a clear expression of their will. The abolition of the monarchy was a major turning point in Nepal's history, and it ushered in a new era of hope and promise for the country.
6. 1963: A cyclone in the Bay of Bengal killed over 22,000 people in India and Bangladesh.
- The cyclone formed on May 22, 1963, in the Bay of Bengal.
- It quickly intensified and reached its peak intensity on May 24, with winds of up to 193 km/h (120 mph).
- The cyclone made landfall in India and Bangladesh on May 26.
- The storm surge caused extensive flooding in coastal areas, and the high winds destroyed homes and crops.
- An estimated 22,000 people were killed in the cyclone, and another 500,000 were left homeless.
- The cyclone was one of the deadliest natural disasters in history.
The 1963 Bay of Bengal cyclone was a major tragedy, and it highlighted the vulnerability of coastal communities to cyclones. In the years since the cyclone, India and Bangladesh have taken steps to improve their disaster preparedness, and they have built stronger infrastructure to withstand future storms. However, more needs to be done to reduce the risk of cyclones in the Bay of Bengal region.
Thanks for reading! Remember to like, share, comment. Stay tuned for more!
Subscribe to My Youtube Channel





No comments:
Post a Comment